The Genetic Code Is Best Described as
The genetic code is a. Which best describes the genetic code Other questions on the subject.

Genetic Code Definition Characteristics And Exceptions
Once again Asimov is at his best this time explaining DNA and the underlying genetic code in an easy to understand manner.

. 8 8 4 2 1 0. Both ambiguous and redundantd. AnsweraTextbook Reference143 How Is the Information Content in DNA Transcribed to.
DNA is made up of 4 nucletotides. A gene is a segment of DNA a condensed DNA molecule makes up a chromosome a chromosome is inside a nucleus and a nucleus is contained within a cell. In particular this last result implies the partition of the code in two equivalent sets.
Which of the following best describes the degeneracy of the genetic code. The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material DNA or RNA sequences is translated into proteins amino acid sequences by living cells. The genetic material of an offspring of sexually reproducing organisms is best described as genes from both parents in unique combinations.
The three codons in the genetic code that do not specify amino acids are called a. Genetic code is redundant because. None of the above.
Nucleotides are the building blocks of. Redundant but not ambiguous. How water is moving through the ecosystem.
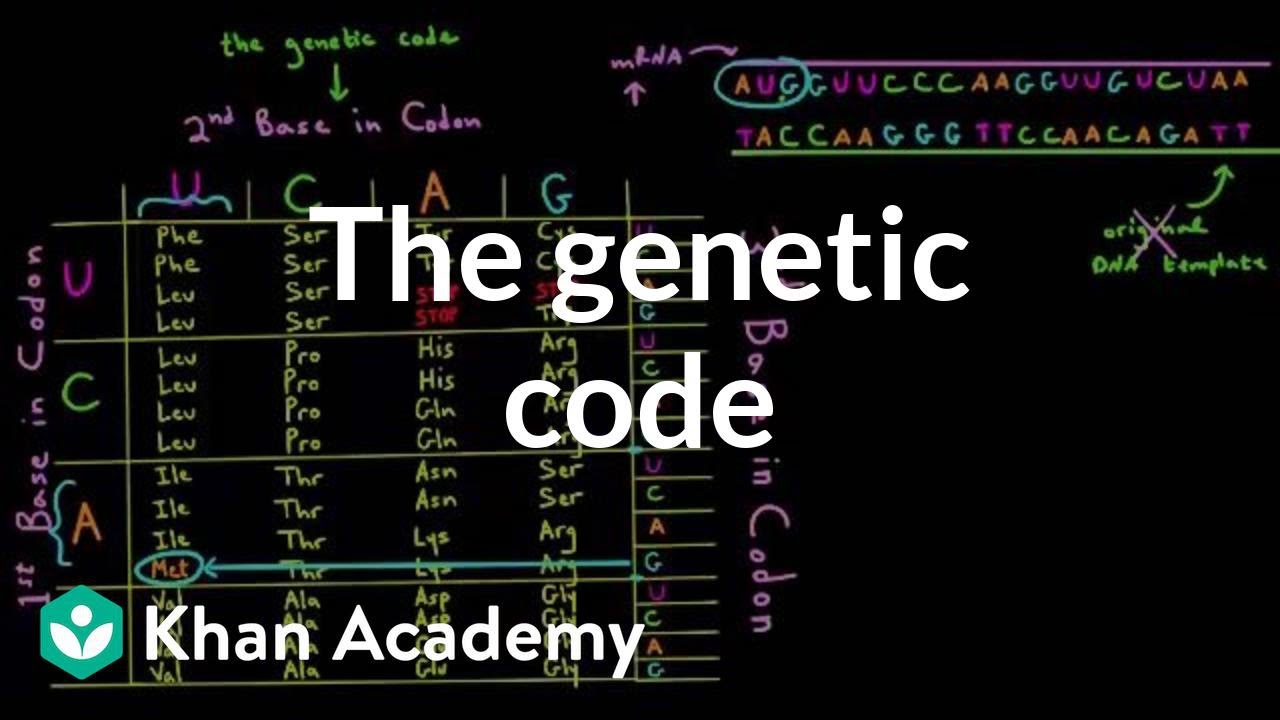
The instructions in a gene that tell the cell how to make a specific protein. Adenine A Thymine T Guanine G Cytosine C whether in a bacteria or in a human which is what makes it universal. The genetic code is called a universal code because all known organisms use the same four nucleotide bases.
He starts with the fundamentals of the language of chemistry the symbols for the elements diagrams of molecules and the basics of. The order of the nucleotides A T C and G is what makes up genes and determine what. O neither ambiguous nor redundant.
6 codon1 amino acid D. Neither ambiguous nor redundant. They show that neither theory is complete and entirely correct.
The four nucleotide bases are adenosine thymidine cytidine and guanosine. Organism differ according to the arrangement of the nucleotide bases. The analysis of the euplotid nuclear genetic code leads to the unique solution.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION sarahjackson6456 sarahjackson6456. CAM plants have adapted to very dry climates by opening their stomata only during the day. Neither ambiguous nor redundant.
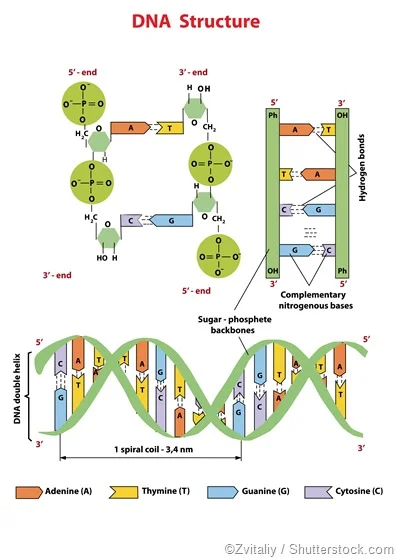
This genetic information is DNA a double-stranded molecule made of strings of nucleotides. The genetic code refers to DNA which is like a blueprint that can be found in all living organisms. Everything in our cells is.
They show that scientists will never agree on where the moon came from. Ambiguous but not redundant. Read 22 reviews from the worlds largest community for readers.
A C G and T are the letters of the DNA code. A gene is a segment of DNA a condensed DNA molecule makes up a chromosome a chromosome is inside a nucleus and a nucleus is contained within a cell. 1 codon 6 amino acid C.
The genetic code is best described as a. The same analysis for the vertebrate mitochondrial genetic code leads to the unique solution. Each genes code combines the four chemicals in various ways to spell out three-letter.
O redundant but not ambiguous. It is typically discussed using the codons found in mRNA as mRNA is the messenger that carries information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. DNA molecules condense to form chromosomes during certain stages of the cell cycle.
Expert Answer 100 5 ratings Redundant but not ambiguous is the correct answer. Ambiguous but not redundant. A DNA molecule is a segment of a gene a gene makes up a chromosome a chromosome is inside a cell and a cell is contained within a nucleus.
They show that more experiments on moon formation need to be done. Three bases form an amino acid also known as a codon. They stand for the chemicals adenine A cytosine C guanine G and thymine T respectively that make up the nucleotide bases of DNA.
Both ambiguous and redundant. 8 7 4 2 1 1. The genetic code is best described as a.
Biology 22062019 0800 ramseynikki87. Both ambiguous and redundant. The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material DNA or RNA sequences is translated into proteins amino acid sequences by living cells.
They show that no theory accounts for the existence of the moon. The genetic code is the code our body uses to convert the instructions contained in our DNA the essential materials of life. Genetic Code Definition.
The storage of the genetic code can be describes as a zone where your DNA lies and is kept until sexual reproduction. In this lesson explore the genetic code how mitosis and meiosis use these instructions and the. These nucleotide sequences form genes which are segments of DNA that code for proteins.
Redundant in prokaryotes but ambiguous in eukaryotes. Redundant but not ambiguous. Ambiguous but not redundant.
Biology 22062019 0400 deee12345. The genetic code is best described as. The genetic code is a set of rules defining how the four-letter code of DNA is translated into the 20-letter code of amino acids which are the building blocks of proteins.
The Genetic Code book. 1 codon 1 amino acid B. Both DNA and RNA.
Redundant but not ambiguousb. Neither ambiguous nor redundant. A gene is a segment of.
O ambiguous but not redundant. The genetic code once thought to be identical in all forms of life has been found to diverge slightly in certain organisms and in the mitochondria of some eukaryotes. The flow of information in a cell is best described as DNA is transcribed to mRNA the information in mRNA is then translated into a sequence of amino acids in a ribosome.
Which best describes the storage of the genetic code. In a eukaryotic cell that is going to make a protein used to regulate glycolysis translation will take place In a free floating ribosome in the cytoplasm. The genetic code is best described as O both ambiguous and redundant.
The genetic code is the instruction that a gene uses to tell a cell how to make a specific protein. The distribution of related animals and plants across the world. See box 1 and.
View the full answer Transcribed image text.

Protein Synthesis Translation Microbiology

Genetic Code Genetic Tables Properties Of Genetic Code
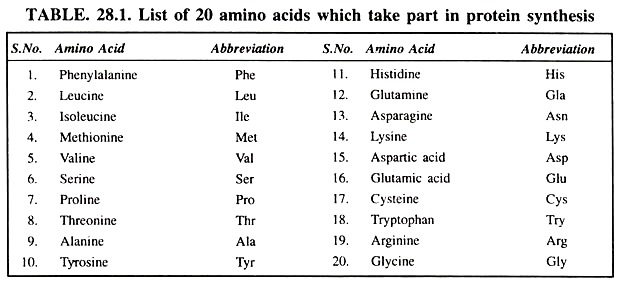
Genetic Code Meaning Types And Properties
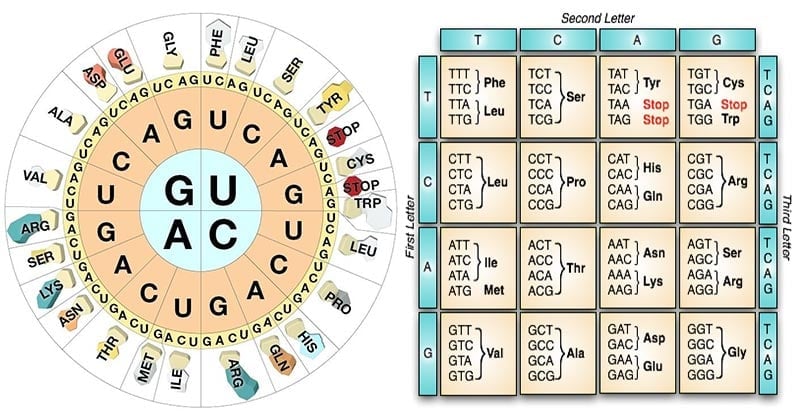
Characteristic Of Genetic Code

Genetic Code Definition Characteristics And Exceptions
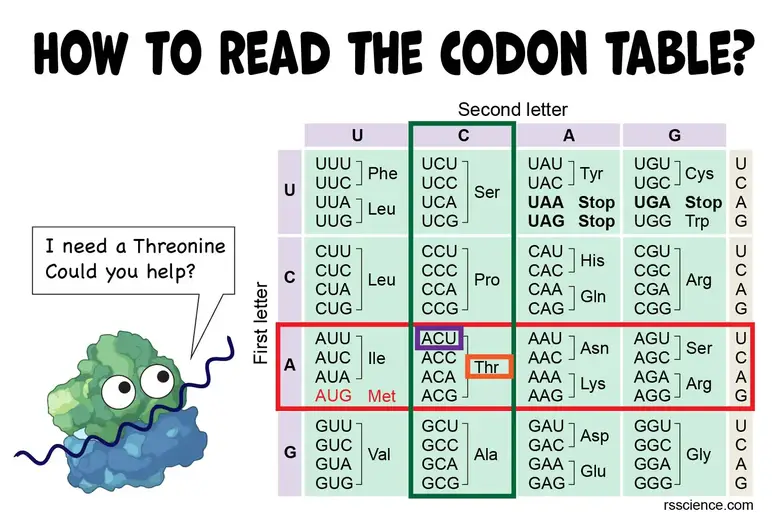
How To Read The Amino Acids Codon Chart Genetic Code And Mrna Translation Rs Science

Francis Crick And The Discovery Of The Genetic Code Learn Science At Scitable

Protein Synthesis Ck 12 Foundation

Overview Of Translation Article Khan Academy

6 Questions About Dna Answered Britannica

6 Questions About Dna Answered Britannica
4 6 Genetic Code Biology Libretexts
The Genetic Code Boundless Biology

Francis Crick And The Discovery Of The Genetic Code Learn Science At Scitable

Characteristics Of The Genetic Code A Level Biology Revision Notes
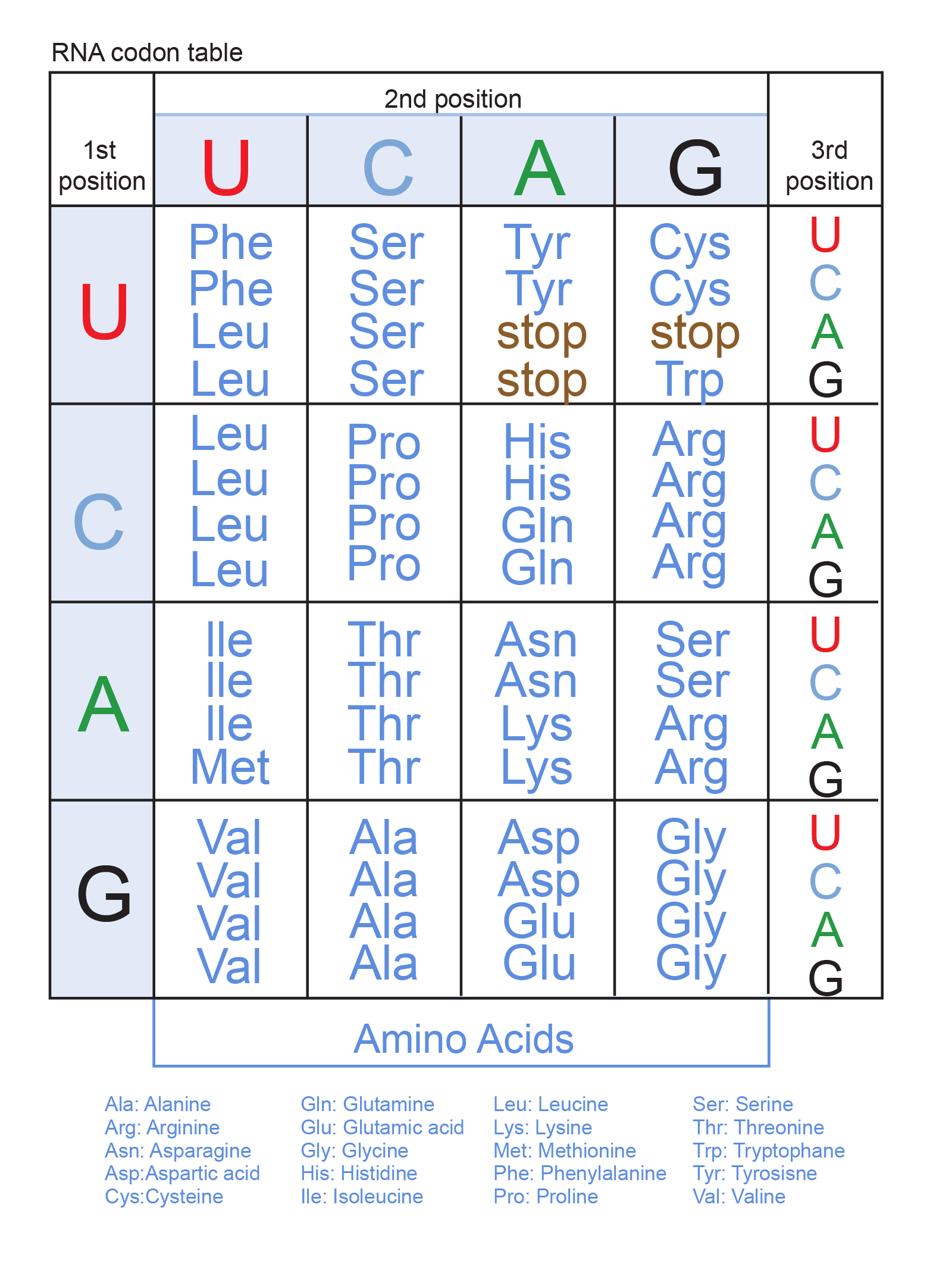

Comments
Post a Comment